New Features in PERMAS Version 18
The new Version 18 of PERMAS is available since July 2020.
See also product description
The version number of VisPER now equals the PERMAS Version in order to ship a
consistent package.
An PERMAS for Education (PERMAS4EDU) is available for training and education purposes. See PERMAS4EDU
- PERMAS V18 continuously offers improved computing performance:
-
- The iterative solver for frequency response analysis has been accelerated significantly. Moreover, the SOLV=SMW option has been generalized, e.g. to support control elements.
- The runtime for contact analysis of large models has been reduced once again.
- The nonlinear stress computation is now parallelized, as well as capacity and conductivity for heat transfer.
- Besides Kepler, also Pascal and Volta graphic cards are supported by the PERMAS Module XPU. Cuda 10.1 is recommended.
- The HDF import of VisPER has been significantly accelerated.
- New Modules
-
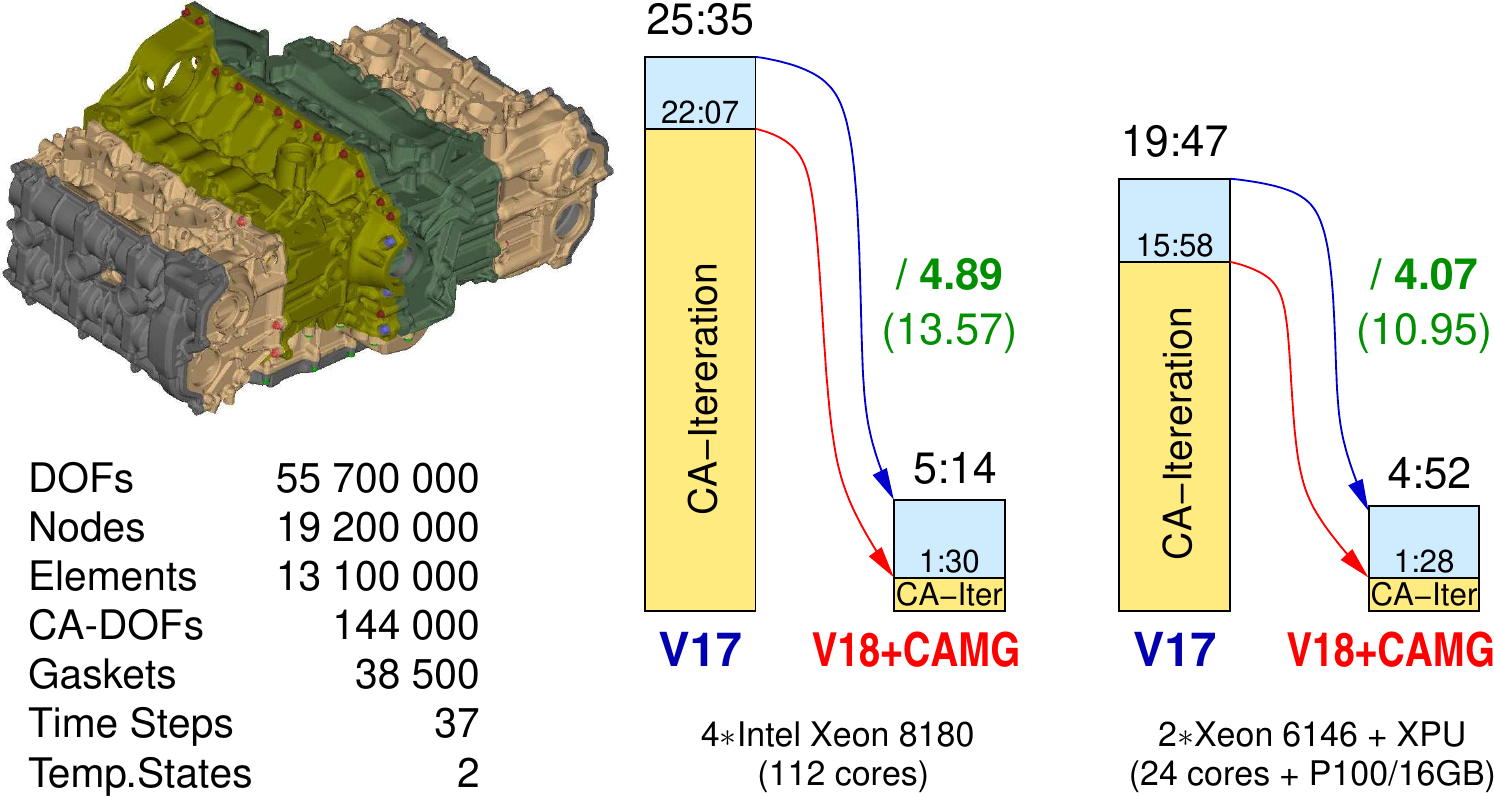
- A new generation of contact solvers is delivered with the CAMG module, that enables high performance gains for larger contact and/or structural mechanics models. Model sizes with more than 180 Mio dofs have been computed. This establishes the third generation of INTES contact solvers as completely independent technology branch.
- The NLSA module provides functionality to compute large strain problems (hyperelastic material behavior).
- Major extensions
-
- Extensions to Basic Module (Module MQA):
- The use of encrypted material data is now possible.
- Local systems ($RSYS) may use names and a description in addition to the former ID. Moreover, reference points may be defined via node sets. If the set contains more than one node, the center of gravity is computed automatically.
- Revision of MPCs
- MPCs may be defined also in the CONSTRAINTS variant. Thus, a large variety of new option such as, change between contact and fixed (tight) coupling or CONTLOCK arises, as well as new options for sampling and optimization.
- New MPC NODE with general coupling directions (non ROTB).
- MPC ISURFACE also with general coupling directions and extra guiding node for relative distance measure.
- Automatic over-constrained handling of MPCs and MPC labels (name/text/id).
- The inertia relief command has been extended. With REFERENCE = CENTER/RIGMODE you may choose the non-moving reference as COG or for the chosen rigid body modes definitions. Moreover, nonsymmetric loads ($LCMATRIX) are supported (i.e. aerodynamic loads).
- Extensions for Dynamics.
- Improved handling of rigid body modes.
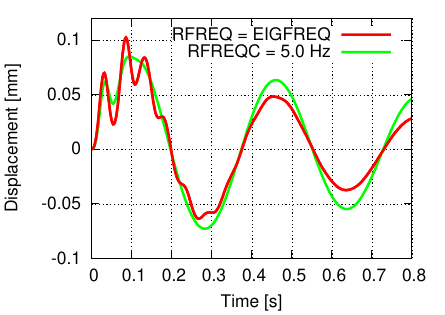
- Frequency dependent loads ($FREQLOAD) may be specified as prescribed accelerations/velocities.
- For modal timehistory response, initial displacements and velocities may be defined via $INIVAL.
- The equivalent viscous damping for modal timehistory response may be computed for each eigenfrequency instead of using a constant reference frequency.
- Extensions to Nonlinear Static Analysis (Module NLS):
- Nonlinear computation of transversly isotropic short fibre materials.
- Improved stability of MPC-Update & NLGEOM=yes (lever arm correction) and for $MPC WLSCON.
- NLLOAD time steps are respected as $NRESULT for TIME=ABS.
- A new UCI switch: NLITSTATE is available to output out-of-balance forces and displacements to be able to investigate convergence problems.
- Extensions to Linear Buckling Analysis (Module BA):
- New solver with automatic shift.
- Optional choice of sign for buckling mode factors.
- Also possible in combination with OPT/TOPO.
- Extensions to Parametric Design Optimization and Topology Optimization (Modules OPT and TOPO):
- Buckling analysis is supported for both: Shape and Topology Optimization.
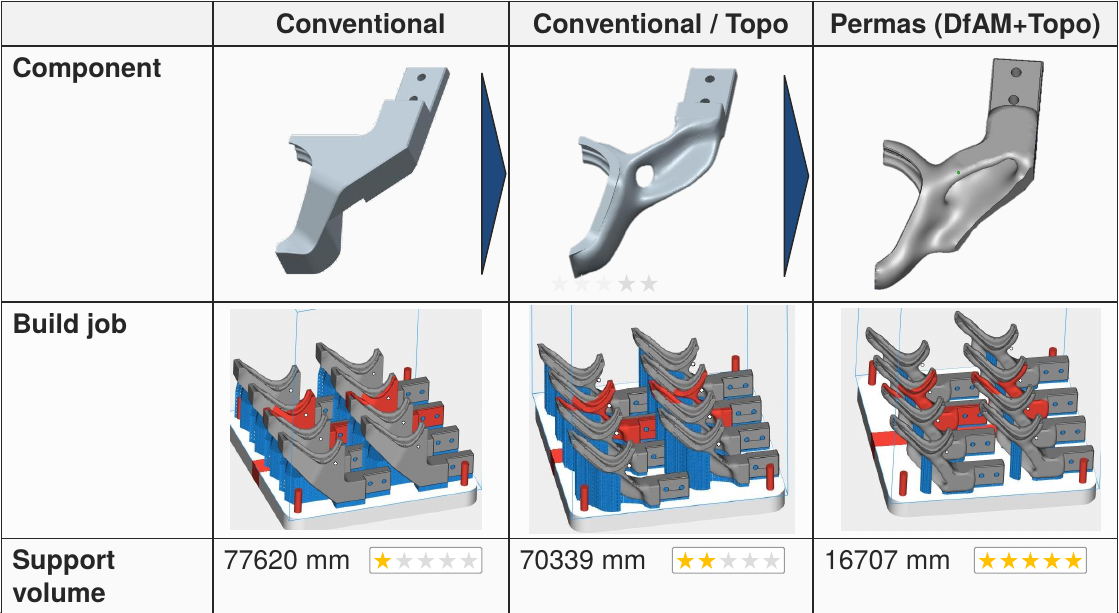
- Improved handling of manufacturing conditions for TOPO and global convergent ACP algorithm.
- Specific 3D printing conditions (e.g. overhang angle, needed support volume).
- Improved shape modification directions and improved mesh relaxation as well as new solver for freeshape.
 Digitization for Additive Manufacturing (DfAM)
Digitization for Additive Manufacturing (DfAM) - Extensions to Basic Module (Module MQA):
- Other extensions
- Many smaller extensions of almost all functional modules had been performed in addition. Moreover, all interfaces were updated and
adapted to the new functionalities. Most important interface enhancements are:
- Medina
- Support of zero force elements together with Medina 9.0.4.1.
- Support of physical description label (Export PARAM: MEDINA RESLABEL)
- Abaqus
- Support of part instances,
- Large strain elements and hyperelastic material support,
- Abadoor report generation in VisPER to provide a translation overview in .pptx and .xlsx format.
- Excite
- Support of EXCITE binary format ’exb’ (now default) – inclusive interface speedup due to parallel calculation of mass invariants (e.g. 27.5h −→ 7.3h),
- Response results from EXCITE can be imported in PERMAS to perform further calculations.
- I-DEAS
- Support of I-DEAS Master Series Export (e.g. for SimCenter)
For all system platforms an update to the current release of the operating system had been performed.
The INTES PYTHON environment has been updgraded to Python 3.0. The pyINTES Tools have been extended.